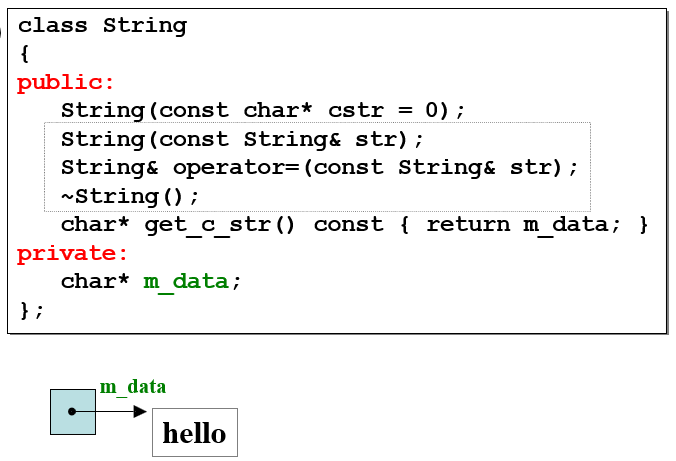
-
析构函数:
~String(); -
拷贝构造函数 copy ctor :
String (const String& str);——string s3(s1) -
拷贝赋值函数 copy op= :
String& operator=(const String& str);——s3=s2编译器默认的拷贝构造赋值(一个bit一个bit的复制),编译器默认的只是拷贝了指针(浅拷贝),而不是指针指向的数据
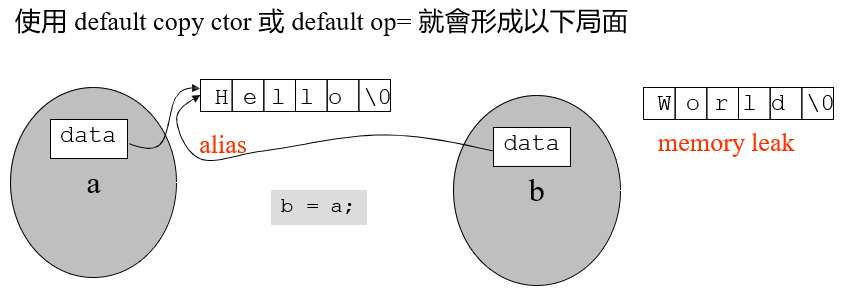
alias(别名)和 memory leak(内存泄漏)都是十分危险的
因此,如果类中有指针,一定自己写这两个函数
6.1 ctor 和 dtor (构造和析构函数)
6.1.1 ctor 构造函数
这里的 new 是申请的字符串的空间
inline
String::String(const char* cstr = 0)
{
if (cstr) { // 指定了初值—— String s2("hello");
m_data = new char[strlen(cstr) + 1]; // 字符串长度 + /0
strcpy(m_data, cstr);
}
else { // 未指定初值—— String s1();
m_data = new char[1];
*m_data = '\0';
}
}
这里的 new 是申请的指针的空间,String()里面还有一个 new
String* p = new String("hello");
delete p;
6.1.2 dtor 析构函数
inline
String::~String()
{
delete[] m_data;
}
每个 new 都对应一个 delete —— 一定要释放
类对象死亡的时候(离开作用域),析构函数会被自动调用
例:这里结束会调用三次 dtor
{
String s1(),
String s2("hello");
String* p = new String("hello");
delete p;
}
6.2 copy ctor 拷贝构造函数
inline
String::String(const String& str)
{
m_data = new char[strlen(str.m_data) + 1]; // “str.m_data” 兄弟之间互为友元
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data); // 深拷贝
}
String s1("hello ");
String s2(s1);
6.3 copy op= 拷贝赋值函数
-
先杀死调用者
-
重新申请指定大小的空间
-
复制字符串内容到调用者
inline
String& String::operator=(const String & str)
{
if (this == &str) // 检测自我赋值 self assignment
return *this;
delete[] m_data; // 第一步
m_data = new char[strlen(str.m_data) + 1]; // 第二步
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data); // 第三步
return *this;
}
一定要在开始就检测自我赋值,因为
a=a时第一步delete了后,会使第三步出现问题