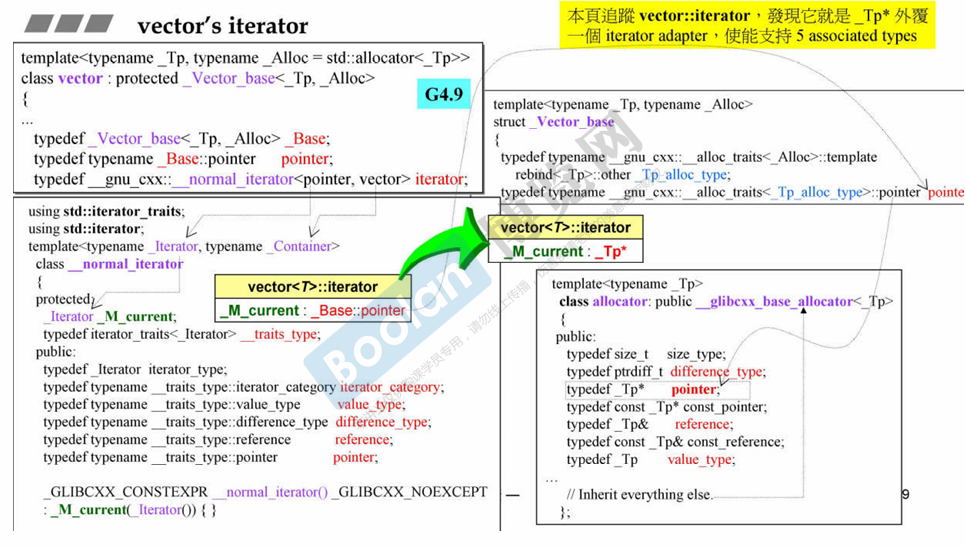
3.1 容器结构分类
分类:序列式容器 Sequence Container,关联式容器 Associative Container
-
序列式容器:按照放入的次序进行排列
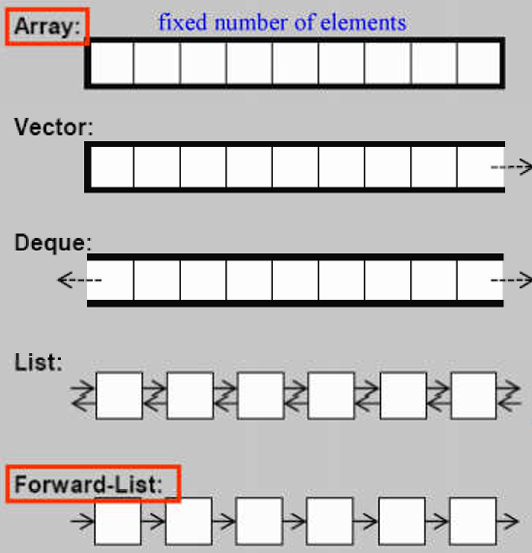
- Array 数组,固定大小
- Vector 向量,会自动扩充大小
- Deque 双向队列,双向都可以扩充
- List 链表,双向链表
- Forward-List 链表,单向链表
-
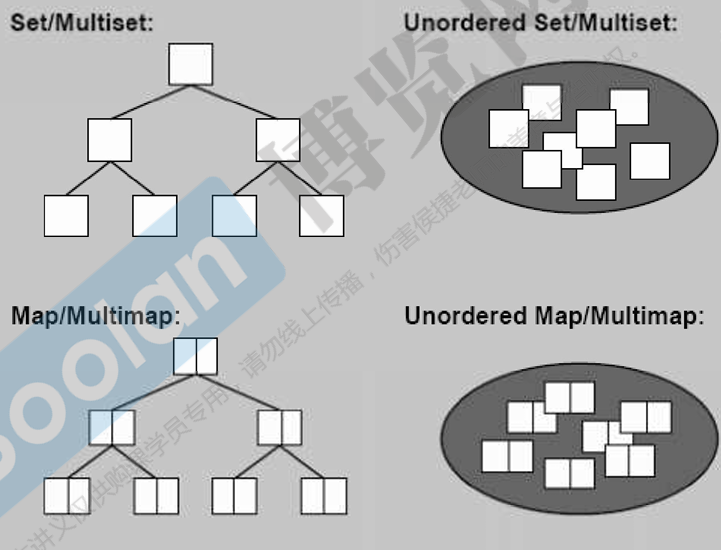
关联式容器:有 key 和 value,适合快速的查找
STL中实现使用红黑树(高度平衡二叉树)和哈希表
-
Set,key 就是 value,元素不可重复
-
Map,key 和 value 是分开的,元素不可重复
-
Multi~,元素是可以重复的
-
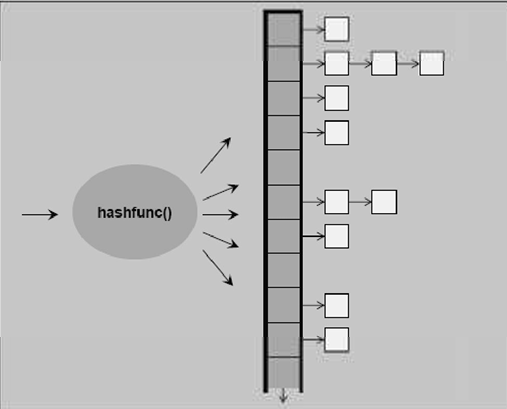
Unordered~,HashTable Separate Chaining
-
其中 Array,Forward-List,Unordered~ 都是C++11的
3.2 序列式容器
3.2.1 array
测试
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib> //qsort, bsearch, NULL
void test_array() {
cout << "\n test_array().......... \n";
// 创建一个包含long型元素的array容器,ASIZE为数组的大小
array<long, ASIZE> c;
// 记录开始时间
clock_t timeStart = clock();
// 填充数组 c 中的元素,使用 rand() 生成随机数
for (long i = 0; i < ASIZE; ++i) {
c[i] = rand();
}
// 输出填充数组所花费的毫秒数
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
// 输出数组的大小、第一个元素、最后一个元素、起始地址
cout << "array.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "array.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "array.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "array.data()= " << c.data() << endl;
// 获取目标值
long target = get_a_target_long();
// 记录开始时间
timeStart = clock();
// 使用标准库的 qsort 函数(快排)对数组 c 进行排序
::qsort(c.data(), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs);
// 使用标准库的 bsearch 函数(二分查找)在排序后的数组中搜索目标值
long* pItem = (long*)::bsearch(&target, c.data(), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs);
// 输出排序和搜索所花费的毫秒数
cout << "qsort()+bsearch(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
// 如果找到目标值,输出该值;否则输出未找到消息
if (pItem != NULL)
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
运行结果:
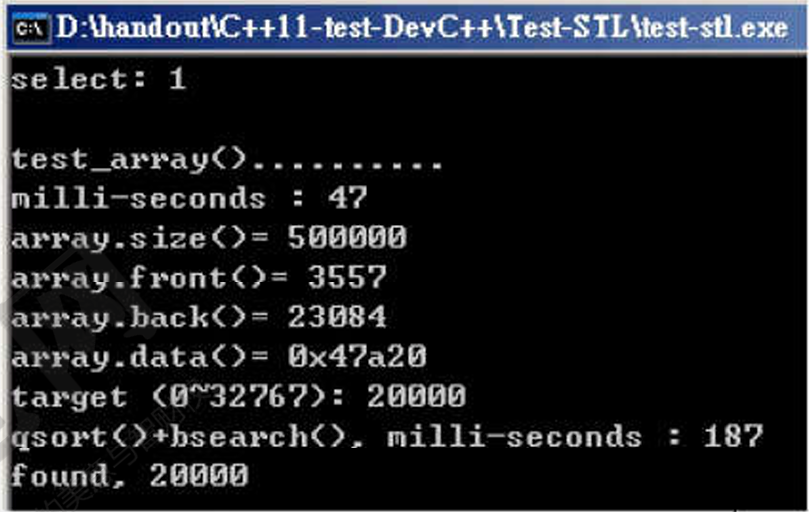
随机数据填充容器:47ms;排序和搜索:187ms
深度探索
C++TR1下(比较简单):
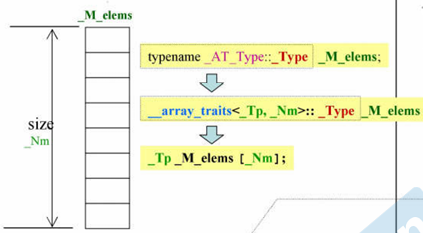
template <typename _Tp, std::size_t _Nm>
struct array
{
typedef _Tp value_type;
typedef _Tp* pointer;
typedef value_type* iterator; // 迭代器为_Tp*
value_type _M_instance[_Nm ? _Nm : 1]; // 如果_Nm为0,就分配一个空间
iterator begin() { return iterator(&_M_instance[0]); }
iterator end() { return iterator(&_M_instance[_Nm]); }
...
};
GCC4.9下(复杂且无益处):
// GCC4.9通过多个typedef以下面的逻辑创建的array里的data
typedef int T[100]; // T即类型int[100]
T c; // 与int c[100]一样
3.2.2 vector
测试

#include <vector>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm> //sort()
// 测试函数,接受一个引用类型的长整型参数
void test_vector(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_vector().......... \n";
vector<string> c; // 创建一个字符串类型的向量
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock(); // 记录开始时间
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i) // 循环插入随机生成的字符串
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand()); // 将随机整数转换为字符串
c.push_back(string(buf)); // 将字符串添加到向量中
} // 这里是处理异常,如内存不够
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
// 输出出现异常的信息以及对应的索引值
// 曾經最高 i=58389486 then std::bad_alloc
abort(); // 异常处理后中止程序
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; // 输出填充向量花费时间
cout << "vector.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; // 输出向量的最大容量
cout << "vector.size()= " << c.size() << endl; // 输出向量的实际大小
cout << "vector.front()= " << c.front() << endl; // 输出向量的首元素
cout << "vector.back()= " << c.back() << endl; // 输出向量的末尾元素
cout << "vector.data()= " << c.data() << endl; // 输出向量地址
cout << "vector.capacity()= " << c.capacity() << endl << endl; // 输出向量的容量
// 直接find来查找————次序查找
string target = get_a_target_string(); // 获取一个目标字符串
{
timeStart = clock(); // 记录开始时间
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); // 在向量中查找目标字符串
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl << endl; // 输出找到的目标字符串
else
cout << "not found! " << endl << endl; // 输出未找到目标字符串
}
// 先排序再二分法查找
{
timeStart = clock(); // 记录开始时间
sort(c.begin(), c.end()); // 对向量中的字符串进行排序
cout << "sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
timeStart = clock();
string* pItem = (string*)::bsearch(&target, (c.data()),
c.size(), sizeof(string), compareStrings);
cout << "bsearch(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != NULL)
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl << endl; // 输出在排序后向量中找到的目标字符串
else
cout << "not found! " << endl << endl; // 输出在排序后向量中未找到目标字符串
}
c.clear(); // 清空向量中的数据
test_moveable(vector<MyString>(),vector<MyStrNoMove>(), value); // 调用另一个函数进行测试
}
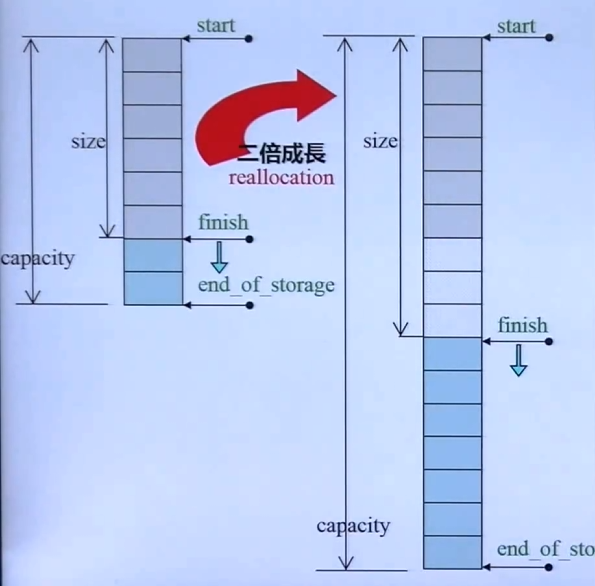
这是 array 在后面插入元素,其中若空间 capacity 不够,其会进行两倍扩充——即空间不够时会将原来的空间 *2
c.push_back(string(buf));
运行结果:
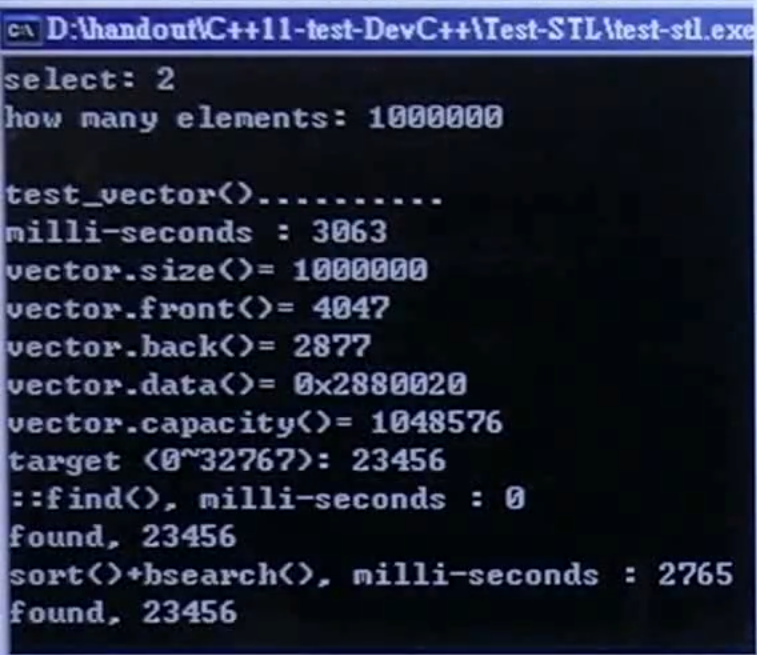
随机数据填充容器:3063ms;直接搜索:0ms(运气很好);排序后二分查找:2765ms
深度探索
GCC2.9下:
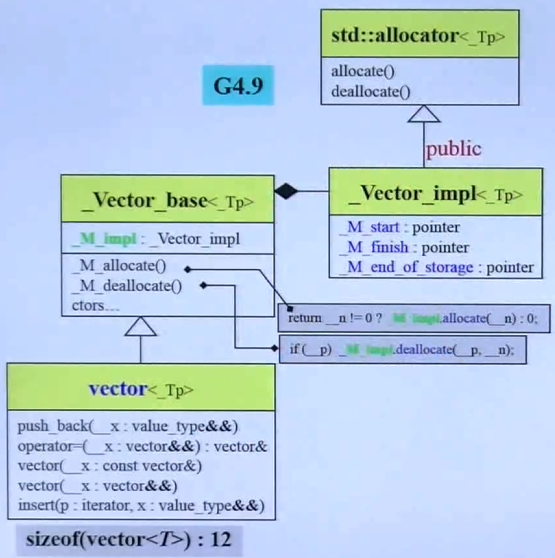
一共3个指针:start,finish,end_of_storage
所以 sizeof(vector<int>) 是12
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class vector
{
public:
typedef T value_type;
typedef value_type* iterator; // 迭代器就是T*
typedef value_type& reference;
typedef size_t size_type;
protected:
iterator start;
iterator finish;
iterator end_of_storage;
public:
iterator begin() { return start; }
iterator end() { return finish; }
size_type size() const { return size_type(end() - begin()); }
size_type capacity() const { return size_type(end_of_storage - begin()); }
bool empty() const { return begin() == end(); }
reference operator[](size_type n) { return *(begin() + n); }
// 所有连续储存的容器都有[]的重载
reference front() { return *begin(); }
reference back() { return *(end() - 1); }
}
vector 每次成长会大量调用元素的拷贝构造函数和析构函数,是一个大成本
void push_back(const T& x)
{
if (finish != end_of_storage) // 还有备用空间
{
construct(finish, x); // 全局函数
++finish;
}
else // 无备用空间
insert_aux(end(), x);
}
template <class T, class Alloc>
void vector<T, Alloc>::insert_aux(iterator position, const T& x){
if (finish != end_of_storage){ // insert_aux还会被其他函数调用所以还有检查
// 在‘备用空间起始处’构建一个元素以vector最后一个元素为初值
// insert_aux也可能被insert调用,元素插入位置不定
construct(finish, *(finish - 1));
++finish;
T x_copy = x;
copy_backward(position, finish - 2, finish - 1);
*position = x_copy;
}
else{
const size_type old_size = size();
const size_type len = old_size != 0 ? 2 * old_size : 1;
// 原大小为0,则分配1;否则,分配原大小的2倍
iterator new_start = data_allocator::allocate(len);
iterator new_finish = new_start;
try{
// 拷贝安插点前的原内容
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start);
construct(new_finish, x);
++new_finish;
// 拷贝安插点后的原内容
new_finish = uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish);
}
catch (...){
destroy(new_start, new_finish);
data_allocator::deallocate(new_start, len);
throw;
}
// 解构并释放原vector
destroy(begin(), end());
deallocate();
// 调整迭代器,指向新vector
start = new_start;
finish = new_finish;
end_of_storage = new_start + len;
}
GCC4.9下变得复杂:
且迭代器也变得乱七八糟,舍近求远,何必如此!!
3.2.3 list
测试
// 同理
void test_list(long& value)
{
...
list<string> c; // 创建一个字符串列表
char buf[10]; // 字符串缓冲区
...
string target = get_a_target_string(); // 获取目标字符串
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); // 在列表中查找目标字符串
cout << "std::find(),milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; // 输出查找时间
...
timeStart = clock();
c.sort(); // 对列表进行排序
cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; // 输出排序时间
c.clear(); // 清空
}
注意:
c.sort();是容器自带的排序函数,如果容器自带肯定是要比全局的排序函数好的list 同样也是用
c.push_back(string(buf));往里添加元素的
运行结果:
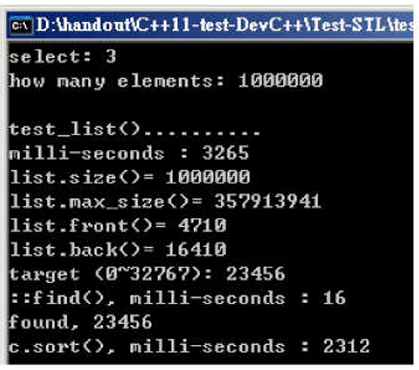
随机数据填充容器:3265ms;直接搜索:16ms;排序:2312ms
深度探索
GCC2.9中
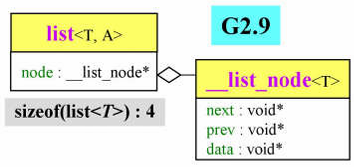
// list class
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class list
{
protected:
typedef __list_node<T> list_node;
public:
typedef list_node* link_type;
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; // 迭代器,每一个容器都会 typedef
// 只传一个参数就行了 不理想
protected:
link_type node; // 一个 __list_node<T> 的指针
...
};
// 节点 class
template <class T>
struct __list_node
{
typedef void* void_pointer; // 每次用还要转换类型 不理想
void_pointer prev;
void_pointer next;
T data;
};
除了 array,vector 这样是连续存储的容器,其他容器的 iterator 都是智能指针,其有大量的操作符重载 —— 模拟指针
基本上所有的 iterator 都有下面5个 typedef 和一大堆操作符重载
// iterator class
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> self;
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category; // (1)双向迭代器
typedef T value_type; // (2)迭代器所指对象的类型
typedef Ptr pointer; // (3)迭代器所指对象的指针类型
typedef Ref reference; // (4)迭代器所指对象的引用类型
typedef __list_node<T>* link_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; // (5)两个迭代器之间的距离类型
link_type node; // iterator本体,一个指向__list_node<T>的指针
reference operator*() const { return (*node).data; }
pointer operator->() const { return &(operator*()); }
self& operator++() // ++i
{
node = (link_type)((*node).next); // 移到下一个节点
return *this;
}
self operator++(int) // i++ 为了区分加上了一个参数其实无用
{
self tmp = *this;
++*this;
return tmp;
}
...
};
注意:self operator++(int){...} 的 self tmp = *this; 中,由于先调用了 = 唤起了 copy ctor 用以创建 tmp 并以 *this 为初值,所以不会唤起 `operator*` —— *this 已经被解释为 ctor 的参数
下面的 ++*this; 同理
与 int 类似:iterator 可以连续前++,但不能连续后++
所以前++是返回引用,后++返回值
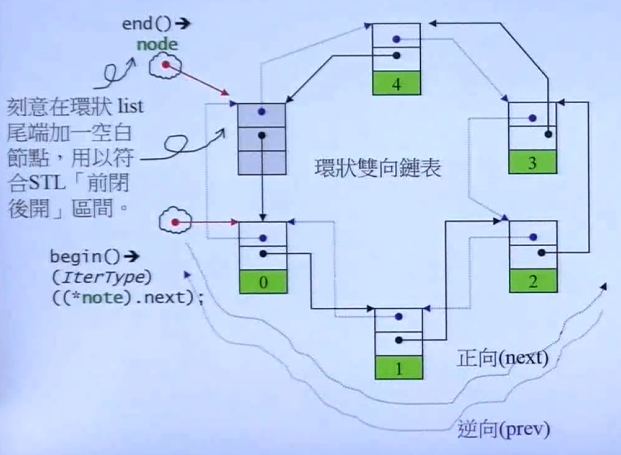
因为要符合前闭后开原则,所以在 list 尾端加上了一个空白节点
GCC4.9中做出了改进:
- 迭代器模板参数从三个 –> 只有一个
- 节点 class 中的前后指针类型从
void*–>_LIst_node_base*
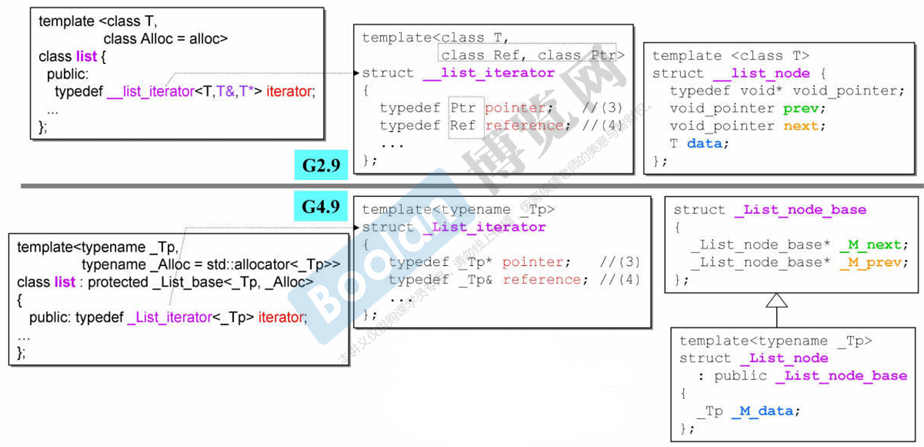
在GCC4.9中 sizeof(list<int>) 是 8
在GCC2.9中 sizeof(list<int>) 是 4
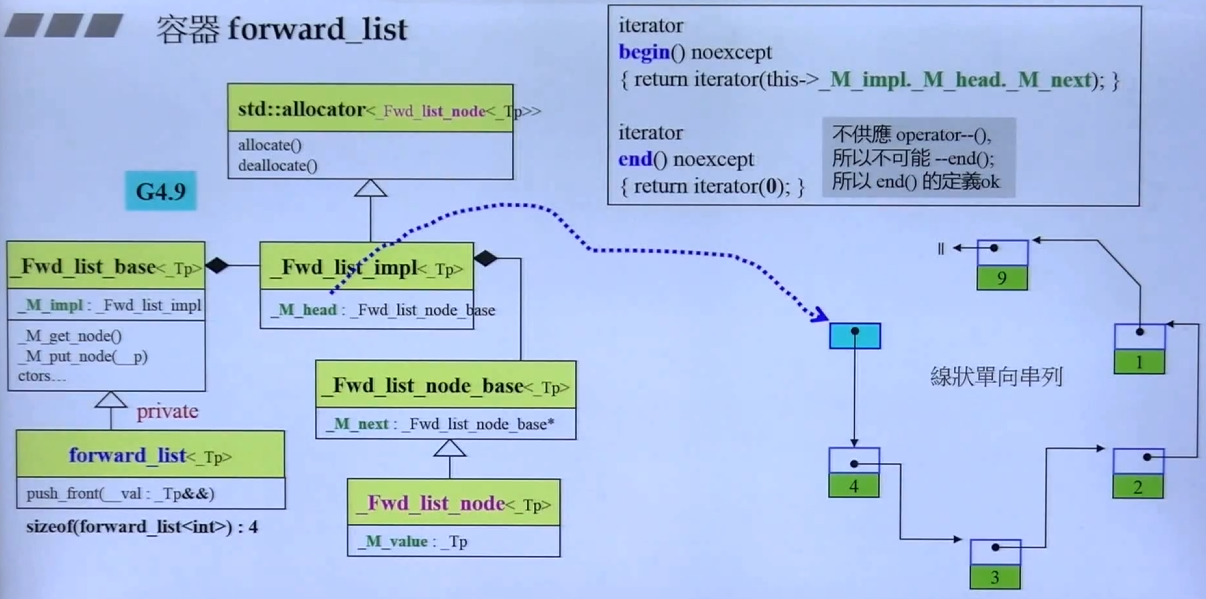
3.2.4 forward_list
测试

// 同理
void test_forward_list(long& value)
{
...
forward_list<string> c; // 创建一个前向列表
char buf[10]; // 字符串缓冲区
...
string target = get_a_target_string(); // 获取目标字符串
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); // 在前向列表中查找目标字符串
cout << "std::find(),milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; // 输出查找时间
...
timeStart = clock();
c.sort(); // 进行排序
cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; // 输出排序时间
c.clear(); // 清空
}
注意:forward_list 只有
c.push_front();且没有forward_list.back()forward_list.size()
运行结果:
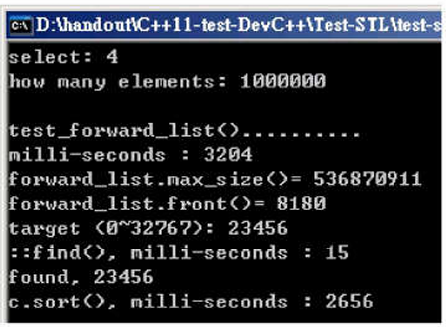
随机数据填充容器:3204ms;直接搜索:15ms;排序:2656ms
深度探索
与 list 相似,略
3.2.6 deque
测试
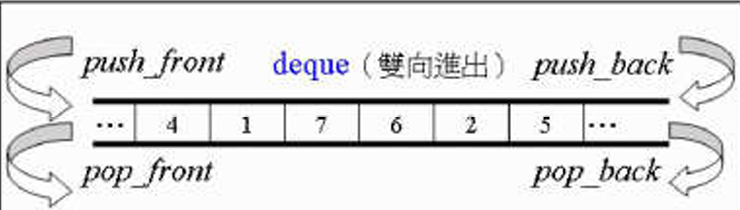
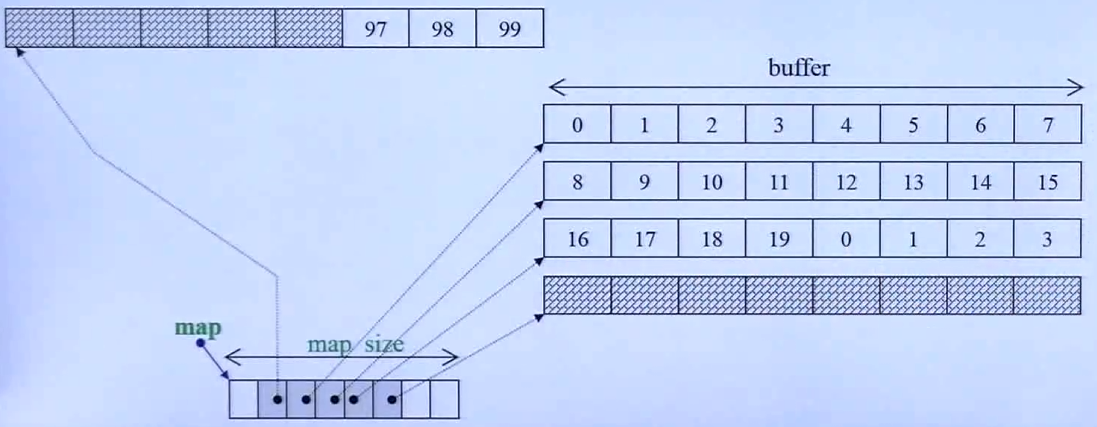
类似vector,两边都能扩充,实际上是分段连续的
其是通过 map(是一个vector,但在扩充时会 copy 到中间)里的指针指向各个 buffer,buffer 里再存数据,每个 buffer 的大小一致,每次扩充都是扩充一个指针指向一个新的 buffer
void test_deque(long& value)
{
...
deque<string> c; // 创建一个双端队列
char buf[10]; // 字符串缓冲区
...
string target = get_a_target_string(); // 获取目标字符串
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); // 在队列中查找目标字符串
cout << "std::find(),milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; // 输出查找时间
...
timeStart = clock();
sort(c.begin(), c.end()); // 对队列进行排序
cout << "sort(),milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; // 输出排序时间
c.clear(); // 清空队列
}
运行结果:
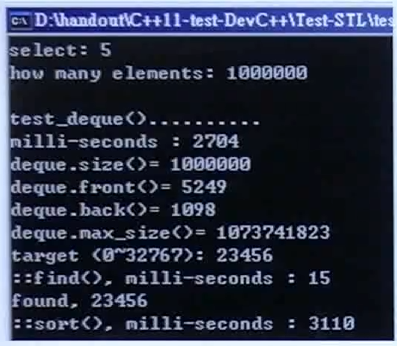
随机数据填充容器:2704ms;直接搜索:15ms;排序:3110ms
下面的 stack 和 queue 内部都是一个 deque,所以技术上这两个可以看作容器适配器 Container Adapter
深度探索
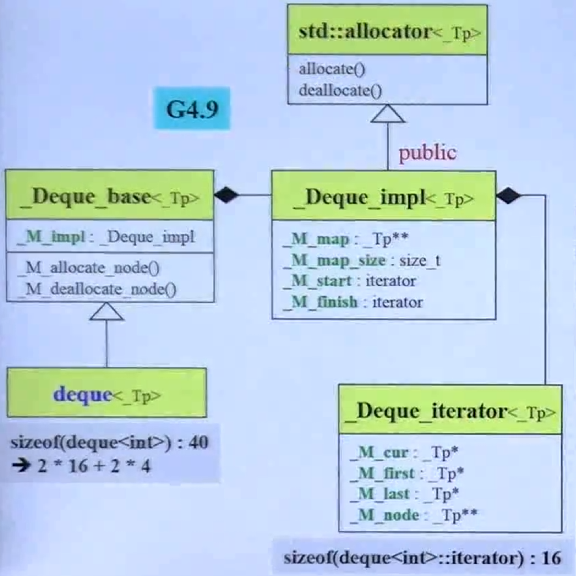
GCC2.9下
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc, size_t BufSiz = 0>
class deque
{
public:
typedef T value_type;
typedef __deque_iterator<T, T&, T*, BufSiz> iterator;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef T* pointer;
protected:
typedef pointer* map_pointer; // T** 指向指针的指针
protected:
iterator start;
iterator finish;
map_pointer map;
size_type map_size;
// 两个迭代器:16*2,一个指针:4,一个size_t:4,一共40字节
public:
iterator begin() { return start; }
iterator end() { return finish; }
size_type size() const { return finish - start; }
...
};
注意:第三个模板参数
size_t BufSiz = 0有一个函数:如果不为0,则 buffer size 就是传入的数据
如果为0,表示预设值,那么
如果
sz = sizeof(value_type)< 512,传回512/sz如果sz = sizeof(value_type)>= 512,传回1
迭代器四个指针,cur 指向当前元素,first 指向当前 buffer 的第一个元素,last 指向当前 buffer 的最后一个元素的下一个,node 指向当前 buffer 在 map(控制中心)的指针
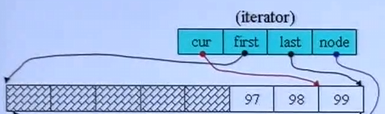
// deque迭代器
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr, size_t BufSiz>
struct __deque_iterator
{
typedef random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category; // (1)
typedef T value_type; // (2)
typedef Ptr pointer; // (3)
typedef Ref reference; // (4)
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; // (5)
typedef T** map_pointer;
typedef __deque_iterator self;
T* cur;
T* first;
T* last;
map_pointer node; // 指向指针的指针
// 四个指针,一共16字节
...
};
deque 中的 insert 函数:
iterator insert(iterator position, const T& x)
{
if (position.cur == start.cur) // 插入点在deque最前端
{ // 交给push_front
push_front(x);
return start;
}
else if (position.cur == finish.cur) // 插入点在deque最尾端
{ // 交给push_front
push_back(x);
iterator tmp = finish;
--tmp;
return tmp;
}
else // 在中间插入
{
return insert_aux(position, x);
}
}
iterator insert_aux(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
difference_type index = pos - start; // 安插点前元素个数
value_type x_copy = x;
if (index < size() / 2) // 安插点前的元素少————搬前面的
{
push_front(front());
...
copy(front2, pos1, front1); // 搬元素
}
else // 安插点后的元素少————搬后面的
{
push_back(back());
...
copy_backward(pos, back2, back1);
}
*pos = x_copy; // 安插点设新值
return pos;
}
deque 模拟连续空间(deque iterator 的功能):
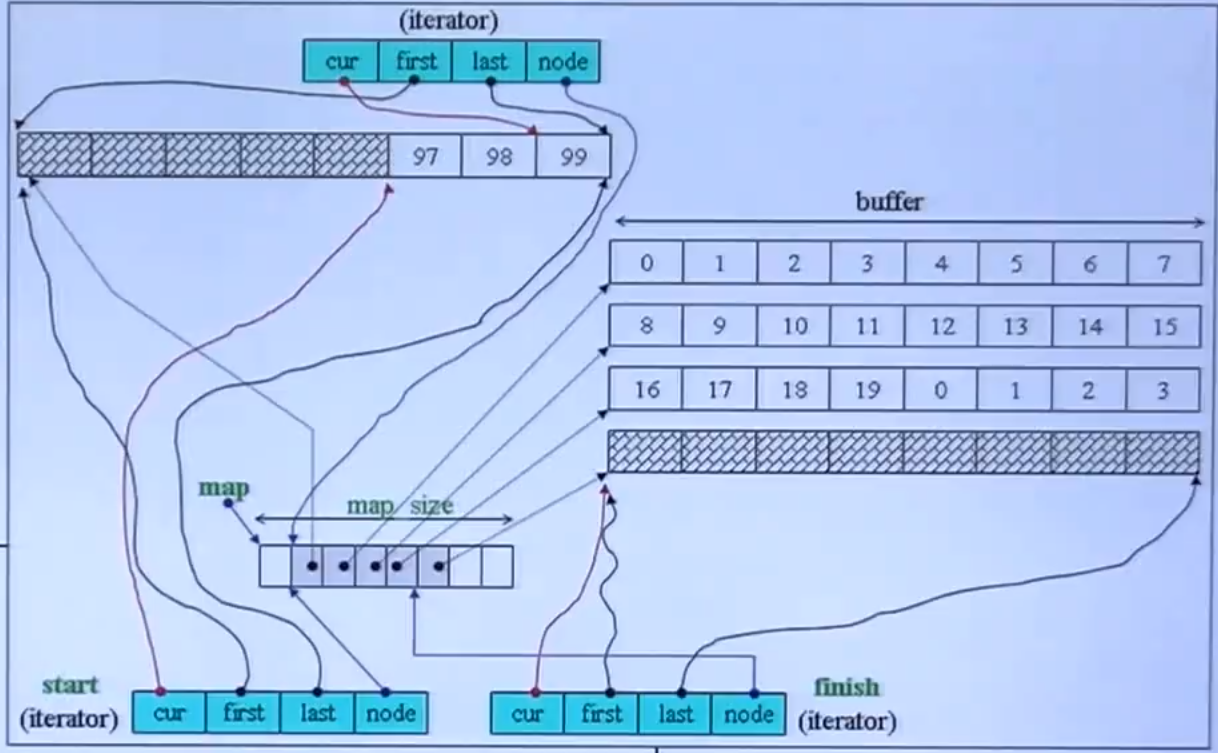
-
-:两个位置之间的距离——前闭后开的元素个数
两个位置之间的距离 = buffer_size * 两个位置之间 buffer 的数量 + 末尾位置到 buffer 前端的长度 + 起始位置到 buffer 末尾的长度
-
++/--:注:下面带参数的是后++(i++)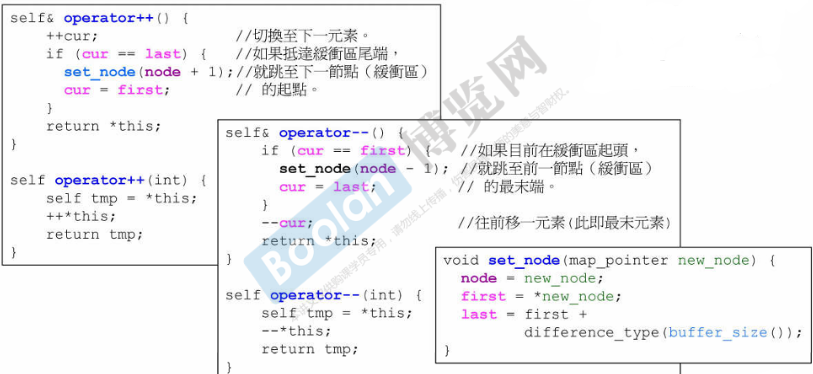
-
+=/+:self& operator+=(difference_type n) { difference_type offset = n + (cur - first); if (offset >= 0 && offset < difference_type(buffer_size())) // 若+了之后在缓冲区大小范围内 cur += n; // 直接移动迭代器 n 步 else { difference_type node_offset = offset > 0 ? offset / difference_type(buffer_size()) : -difference_type((-offset - 1) / buffer_size()) - 1; // 计算偏移的节点数,offset > 0判断是为了之后的-=/- // 这里(-offset - 1)后除buffer_size()再-1是为了offset==buffer_size()的情况 set_node(node + node_offset); // 调整节点,使迭代器指向正确的节点 cur = first + (offset - node_offset * difference_type(buffer_size())); // 调整迭代器位置 } return *this; } self operator+(difference_type n) const { self tmp = *this; // 复制当前迭代器 return tmp += n; // 返回向前移动 n 步后的迭代器副本 } -
-=/-:// -就等于+负的 self& operator-=(difference_type n) { return *this += -n; } self operator-(difference_type n) const { self tmp = *this; return tmp -= n; } -
[]:reference operator[](difference_type n) const { return *(*this + n); }
GCC4.9下:其实没必要这样
G2.91 允许指派 buffer_size
G4.53 不允许了
3.2.7 stack,queque
测试
stack:
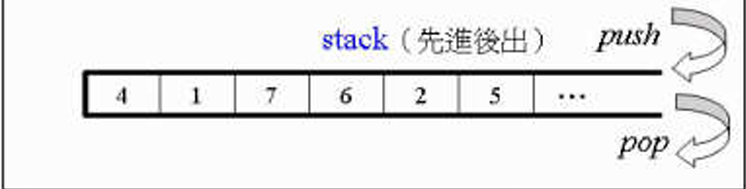
queue:
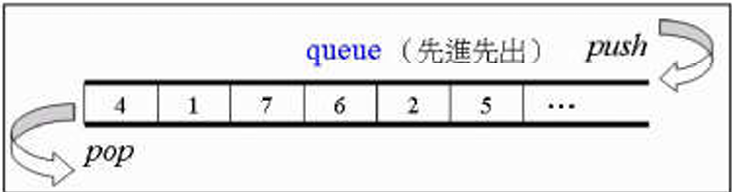
stack,queue 是通过
push()和pop()来放取元素的,且无iterator 的操作
深度探索
stack 和 queue 内部默认用 deque 来实现,所以有时候不会将这两个认为容器而是一个适配器
-
底层函数可以使用 list 和 deque(deque默认更快)
- queue 不能用 vector,stack 可以用 vector
- set,map 都不能用
用时编译器可以通过的,但在具体使用函数时,若遇到底层容器没有这个函数时,就会报错
// queue
template<class T, class Sequence = deque<T>>
class queue
{
...
protected:
Sequence c; // 底层容器
public:
// 都是通过底层容器来实现
bool empty() const { return c.empty(); }
size_type size() const { return c.size(); }
reference front() { return c.front(); }
const_reference front() const { return c.front(); }
reference back() { return c.back(); }
const_reference back() const { return c.back(); }
void push(const value_type& x) { c.push_back(x); }
void pop() { c.pop_front(); }
};
// stack
template<class T, class Sequence = deque<T>>
class stack
{
...
protected:
Sequence c; // 底层容器
public:
// 都是通过底层容器来实现
bool empty() const { return c.empty(); }
size_type size() const { return c.size(); }
reference top() { return c.back(); }
const_reference top() const { return c.back(); }
void push(const value_type& x) { c.push_back(x); }
void pop() { c.pop_back(); }
};
==stack,queue 都不允许遍历,也不提供 iterator==
3.3 关联式容器
3.3.0 RB-Tree
红黑树(Red-Black Tree)是一种自平衡的二叉搜索树 BST(AVL 是另一种)
rb-tree 提供遍历操作和 iterators,按中序遍历遍历,便可以得到排序状态
不能用 iterator 去改变元素的 key(其有严谨的排列规则)
rb-tree 提供两种 insertion 操作:
insert_unique()和insert_equal(),前者表示 key 独一无二,后者表示 key 可重复
GCC2.9下:
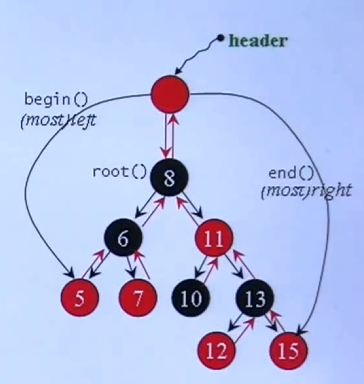
template<class Key, // key的类型
class Value, // Value里包含key和date
class KeyOfValue, // 从Value中取出key的仿函数
class Compare, // 比较key大小的仿函数
class Alloc = alloc>
class rb_tree
{
protected:
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node;
...
public:
typedef rb_tree_node* link_type;
...
protected:
size_type node_count; // rb-tree节点数量,大小4
link_type header; // 头指针,大小4
Compare Key_compare; // key比大小的仿函数,大小1
// sizeof: 9 ——> 12(填充到4的倍数)
...
};
GCC4.9下:
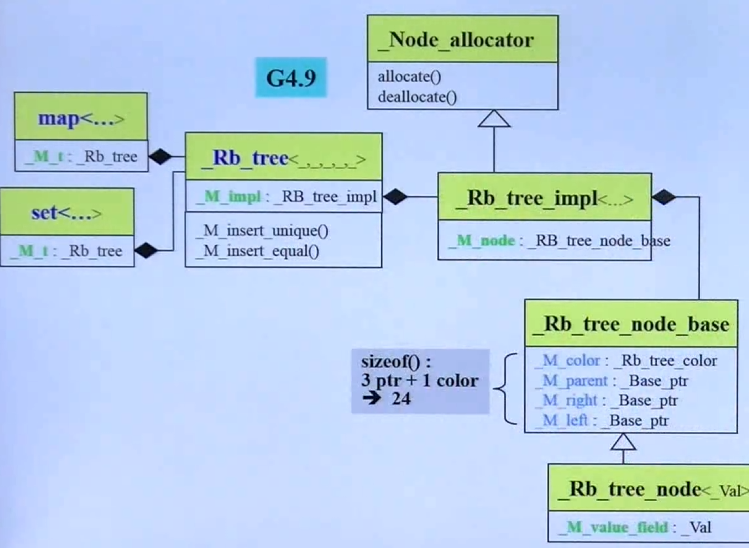
_M_color 是 “枚举”(Enumeration)
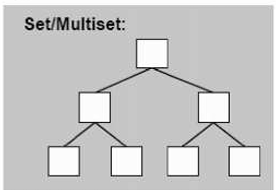
3.3.1 set / multiset
测试
void test_multiset(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_multiset().......... \n";
multiset<string> c; // 创建一个multiset
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock(); // 记录起始时间
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i) // 添加元素到multiset中
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand()); // 将随机数转换为字符串格式
c.insert(string(buf)); // 将字符串插入multiset中
}
catch(exception& p) { // 捕获可能的异常
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl; // 输出异常信息
abort(); // 终止程序
}
}
cout << "毫秒数 : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; // 输出时间差,计算插入时间
cout << "multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl; // 输出multiset大小
cout << "multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; // 输出multiset的最大容量
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); // 在multiset中使用 std::find(...) 查找目标字符串
cout << "std::find(),毫秒数 : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
...
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); // 在multiset中使用 c.find(...) 查找目标字符串
cout << "c.find(),毫秒数 : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
...
}
c.clear(); // 清空multiset
}
安插元素是使用
insert(),其位置由红黑树决定
容器自己有
c.find(),其会比全局的::find()快
运行结果:
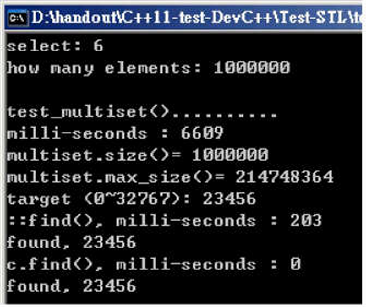
随机数据填充容器:6609ms(其在填充的时候就进行排序了);直接搜索 ::find():203ms;c.find():0ms
深度探索
以 rb-tree 为底层结构,因此有——元素自动排序,key 与 value 和一
set / multiset 提供遍历操作和 iterators,按中序遍历遍历,便可以得到排序状态
禁止用 iterator 去改变元素的值(其有严谨的排列规则)
set的key 独一无二,其
insert()操作用的 rb-tree 的:insert_unique()multiset 的 key 可以重复,其
insert()操作用的 rb-tree 的:insert_equal()
GCC2.9下:
// set
template <class Key, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class set
{
public:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Key value_type;
typedef Compare key_compare;
typedef Compare value_compare;
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type, identity<value_type>,
key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t; // 采用红黑树作为底层机制
public:
typedef typename rep_type::const_iterator iterator;
// 注意:这里是const_iterator,所以不能用iterator改元素
...
};
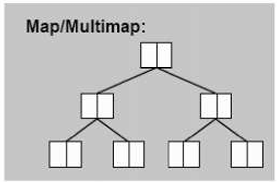
3.3.2 map / multimap
测试
void test_multimap(long& value)
{
...
multimap<long, string> c; // 创建一个multimap,key 为 long 类型,value 为 string 类型
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock(); // 记录起始时间
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i) // 添加元素到multimap中
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand()); // 将随机数转换为字符串格式并复制到缓冲区
// multimap 不可使用 [] 做 insertion
c.insert(pair<long, string>(i, buf)); // 将元素插入multimap中
}
catch(exception& p) { // 捕获可能的异常
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl; // 输出异常信息
abort(); // 终止程序
}
}
cout << "毫秒数 : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; // 输出时间差,计算插入时间
cout << "multimap.size()= " << c.size() << endl; // 输出multimap大小
cout << "multimap.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; // 输出multimap的最大容量
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); // 在multimap中查找目标 key
cout << "c.find(),毫秒数 : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "找到,value=" << (*pItem).second << endl; // 如果找到,输出找到的值
else
cout << "未找到!" << endl; // 如果未找到,输出未找到的信息
c.clear(); // 清空multimap
}
c.insert(pair<long, string>(i, buf));中 key 是从1~1000000,value 是随机取的,将其组合为 pair 插入
运行结果:
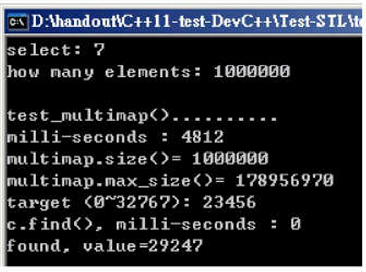
随机数据填充容器:4812ms(其在填充的时候就进行排序了);c.find():0ms
深度探索
以 rb-tree 为底层结构,因此有——元素自动排序
map/ multimap 提供遍历操作和 iterators,按中序遍历遍历,便可以得到排序状态
不能用 iterator 去改变元素的key(其有严谨的排列规则),但可以用 iterator 去改变元素的 data
因此 map / multimap 将 user 指定的 key_type 设定成
const
map的key 独一无二,其
insert()操作用的 rb-tree 的:insert_unique()multimap 的 key 可以重复,其
insert()操作用的 rb-tree 的:insert_equal()
GCC2.9下:
template <class Key, // key的类型
class T, // data的类型
class Compare = less<Key>,
class Alloc = alloc>
class map
{
public:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef T data_type;
typedef T mapped_type;
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
// 注意:这里是const Key ———— 防止改key
typedef Compare key_compare;
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type, select1st<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t; // 采用红黑树作为底层机制
public:
typedef typename rep_type::iterator iterator;
...
};
map 的插入元素有特殊写法:
c[i] = string(buf),其中i就是 key;multimap没有map 的
[]功能:访问元素: 如果指定的键存在于映射中,
map[key]将返回与该键关联的 data;如果键不存在,map[key]将自动创建一个新的键值对,key 为指定的 key,data 为默认 data,并返回这个默认 data
3.3.3 HashTable
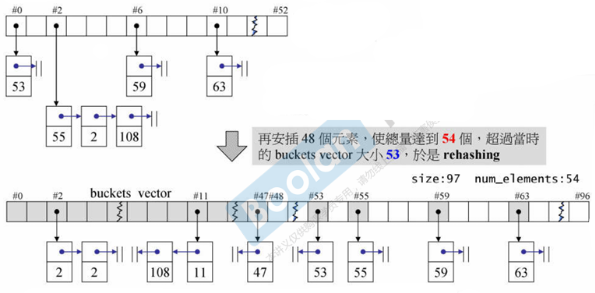
-
元素的位置 = key % bucket大小
-
bucket vector 的大小为质数
-
当元素个数大于 bucket 的总数时,bucket vector 扩充并重新打散放在新计算的 bucket 中(rehashing 很花时间)—— bucket 一定比元素多
在扩充时,按 vector 扩充为2倍大小,但会选择靠进这个数的一个质数做新的大小
GCC2.9下:
template <class Value, // Value里包含key和date
class Key, // key的类型
class HashFcn, // hash函数
class ExtractKey, // 从Value中取出key的方法
class EqualKey, // 判断key相等的函数
class Alloc>
class hashtable
{
public:
typedef HashFcn hasher;
typedef EqualKey key_equal; // 判断key相等的函数
typedef size_t size_type;
private:
// 3个函数对象,大小一共3(应该是0,因为一些因素)
hasher hash;
key_equal equals;
ExtractKey get_key;
typedef __hashtable_node<Value> node;
vector<node*, Alloc> buckets; // vector里3个指针,大小12
size_type num_elements; // 大小4
// 一共19 ——> 20(调整为4的倍数)
public:
size_type bucket_count() const { return buckets.size(); }
};
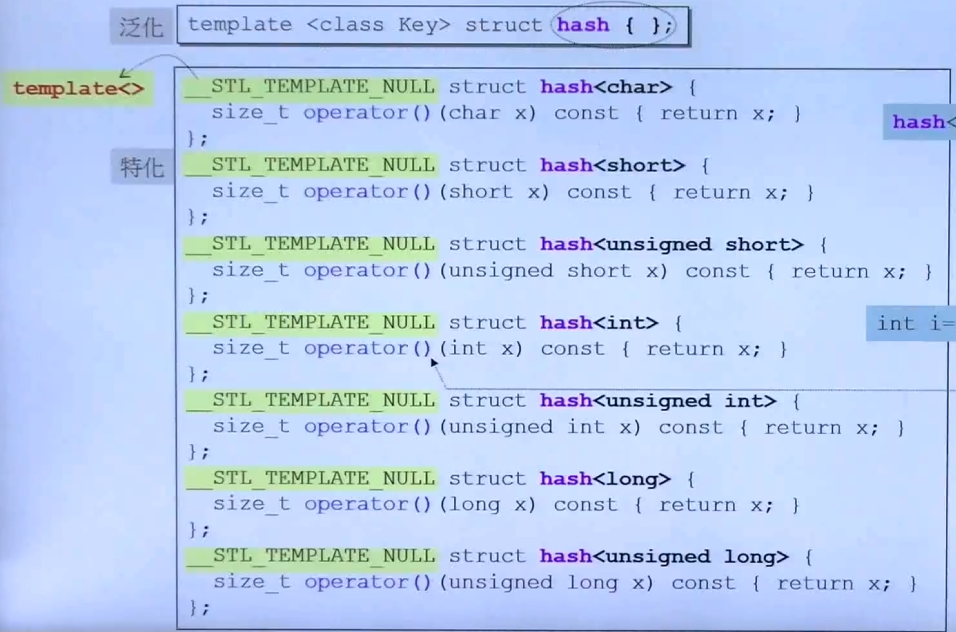
Hash函数:
偏特化写不同类型的 hash 函数,下图都是数值类型,直接返回就可以
下图对 c 风格的字符串做了处理(也可以自己设计),来生成 hash code
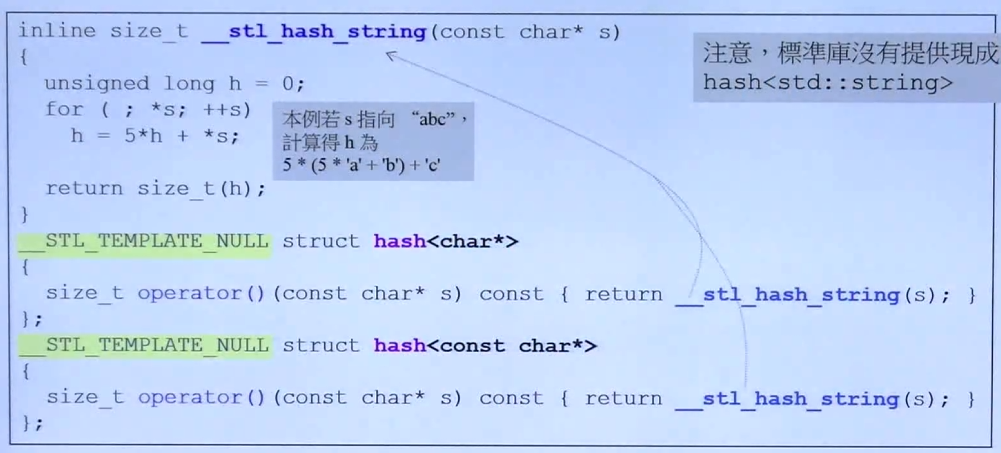
注意:老版本STL没有提供现成的 string 类型的 hash 函数
3.3.4 unordered容器
测试

void test_unordered_multiset(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_unordered_multiset().......... \n";
unordered_multiset<string> c; // 创建一个 unordered_multiset
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock(); // 记录起始时间
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i) // 添加元素到 unordered_multiset 中
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand()); // 将随机数转换为字符串格式
c.insert(string(buf)); // 将字符串插入 unordered_multiset 中
}
catch(exception& p) { // 捕获可能的异常
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl; // 输出异常信息
abort(); // 终止程序
}
}
cout << "毫秒数 : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; // 输出时间差,计算插入时间
cout << "unordered_multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl; // 输出 unordered_multiset 大小
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; // 输出 unordered_multiset 的最大容量
cout << "unordered_multiset.bucket_count()= " << c.bucket_count() << endl; // 输出 unordered_multiset 的桶数量
cout << "unordered_multiset.load_factor()= " << c.load_factor() << endl; // 输出 unordered_multiset 的负载因子
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_load_factor()= " << c.max_load_factor() << endl; // 输出 unordered_multiset 的最大负载因子
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_bucket_count()= " << c.max_bucket_count() << endl; // 输出 unordered_multiset 的最大桶数量
for (unsigned i=0; i< 20; ++i) {
cout << "bucket #" << i << " has " << c.bucket_size(i) << " elements.\n"; // 输出前20个桶中的元素数量
}
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); // 在 unordered_multiset 中使用 std::find(...) 查找目标字符串
cout << "std::find(),毫秒数 : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl; // 如果找到,输出找到的元素
else
cout << "not found! " << endl; // 如果未找到,输出未找到的信息
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); // 在 unordered_multiset 中使用 c.find(...) 查找目标字符串
cout << "c.find(),毫秒数 : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl; // 如果找到,输出找到的元素
else
cout << "not found! " << endl; // 如果未找到,输出未找到的信息
}
c.clear(); // 清空unordered_multiset
}
运行结果:
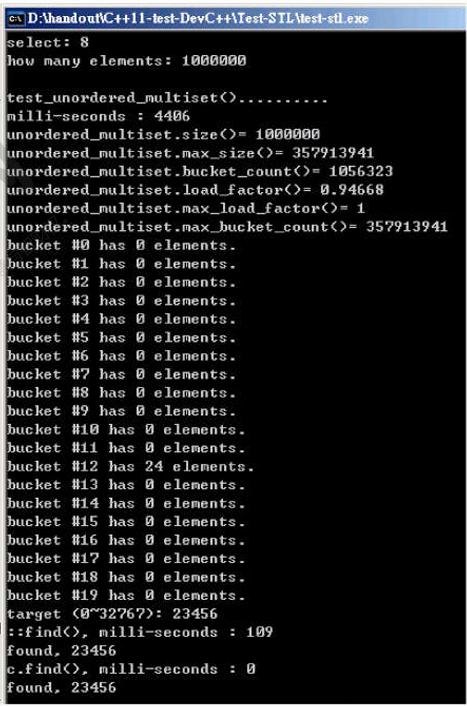
随机数据填充容器:4406ms;直接搜索 ::find():109ms;c.find():0ms;前二十个 bucket 中只有一个有24个元素
深度探索